KEY BENEFITS OF ASPHALT CONSTRUCTION SERVICES IN MELBOURNE WITH INFRA PROJECTS

Experience
As a leading asphalt contractor in Melbourne and Victoria, Infra Projects Group has decades of combined experience in the asphalt industry, with a track record of successfully completing projects of all sizes and complexity.
Efficiency
As a top-tier asphalt solution, we understand the importance of minimising disruptions and downtime, and we work closely with our clients to ensure that our projects are completed on time and within budget.

Quality
We use only the high-grade materials and the latest industry-proven techniques to ensure that our asphalt construction works are built to last.

Safety
Safety is a top priority at Infra Projects Group, and we have strict protocols in place to ensure that all of our asphalt services are completed in a safe and efficient manner.

Expertise
As a leading asphalt contractor in Melbourne and Victoria, our team has the expertise to handle all of your asphalt needs, from minor repairs to major new construction projects.
TYPE OF ASPHALT WORKS
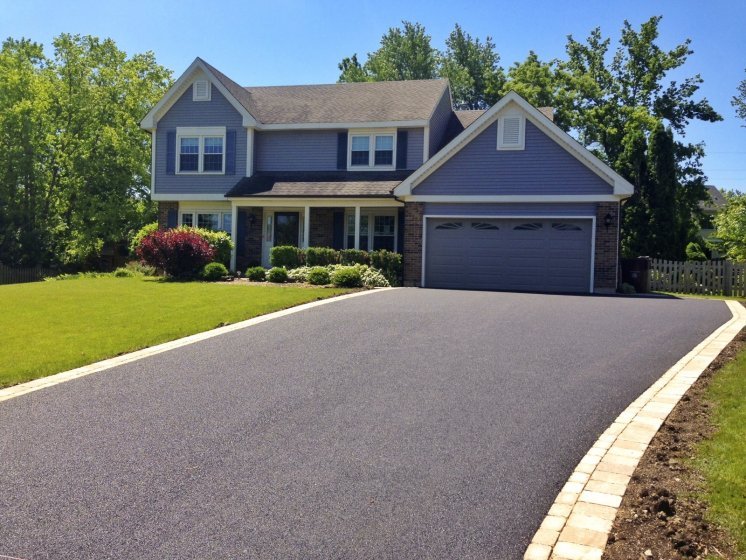
Asphalt Driveways
Asphalt driveways are a popular choice for residential properties because they are relatively economical to install compared to other kinds of driveways. They are also famous for their durability and low maintenance requirements, as they can withstand heavy loads, such as vehicles and foot traffic, and resist cracking and erosion. Additionally, asphalt driveways can be sealed to prevent water from entering the surface and causing harm.
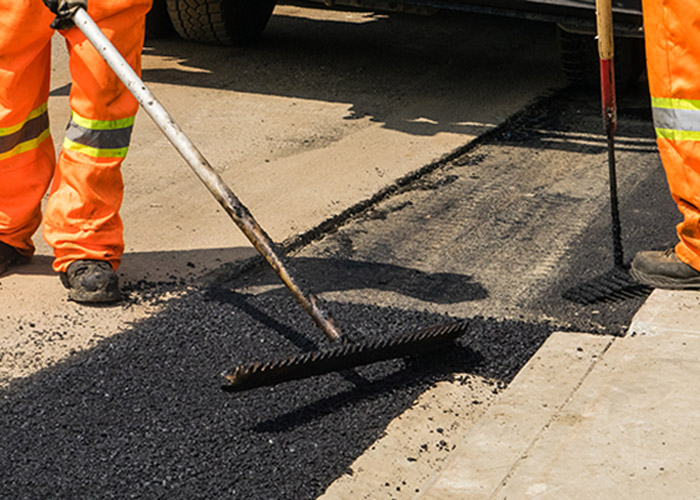


Asphalt Repairs
Asphalt repairs are often necessary to extend the lifespan of an existing asphalt surface. This can include filling in potholes, patching cracks, and smoothing out any hard surfaces. Asphalt repairs can be done with a cold or hot asphalt mix. Appropriate preparation of the surface is a must before any repair is implemented. Repairing asphalt is easier, more convenient, and less time-consuming and costly.
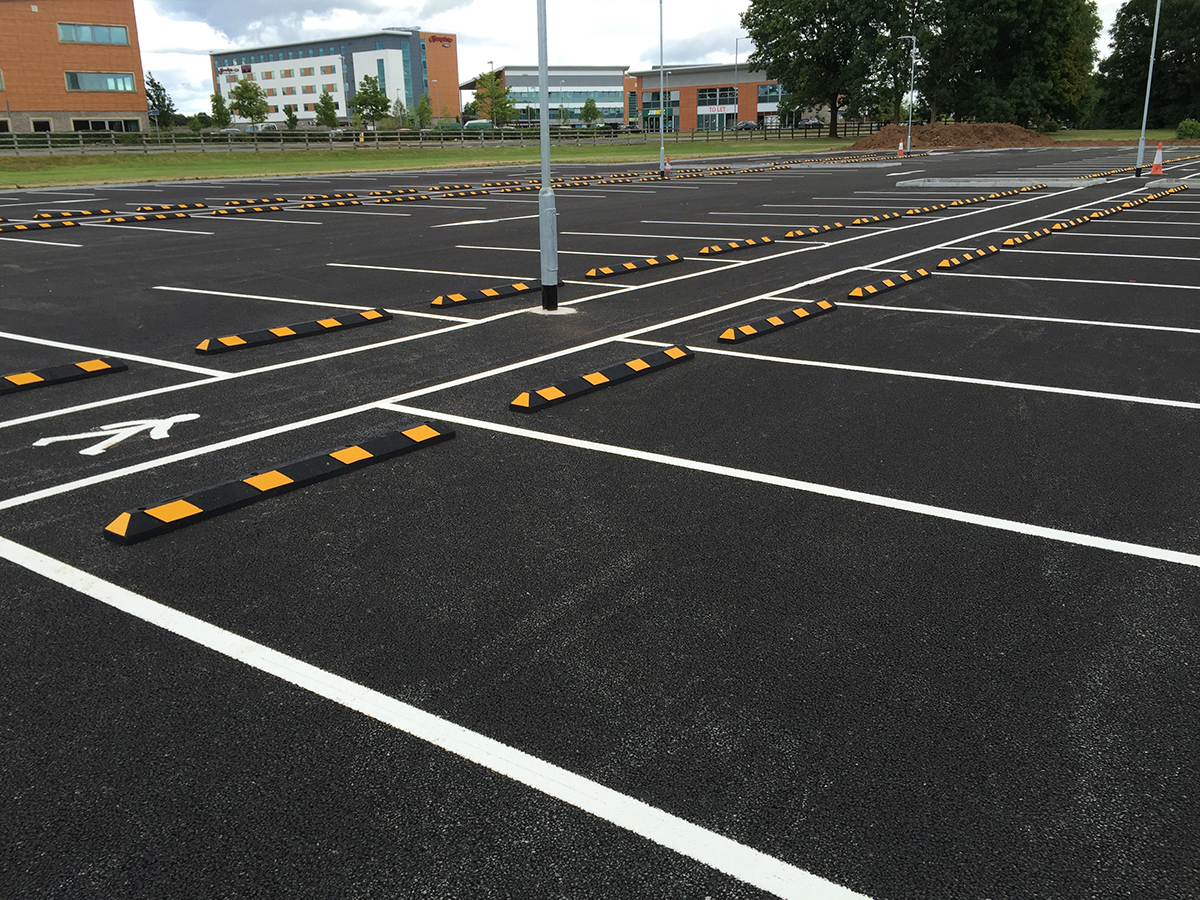
Asphalt Car Park
Asphalt car parks are a popular choice for commercial and industrial properties because they are relatively inexpensive to install, durable, and low maintenance. They can withstand heavy loads, such as vehicles and foot traffic, and resist cracking and erosion. Regular maintenance can prolong the life of the asphalt surface and increase its durability. Proper drainage systems and grading should be in place to ensure water doesn’t pool or cause damage to the asphalt surface.
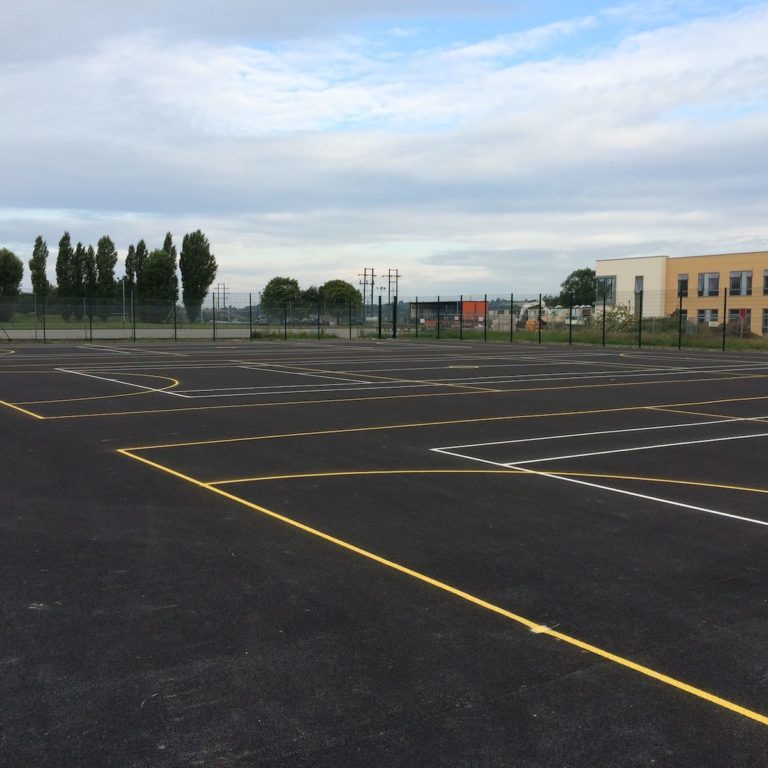


Asphalt School Areas
Asphalt surfaces in schools, such as playgrounds, sports fields, and parking areas, must be maintained regularly to ensure safety and longevity. They are susceptible to damage from intense foot activity as well as typical wear and tear. Regular maintenance, such as filling in potholes, patching cracks, and smoothing out rough areas can prolong the life of the asphalt surface and make it safer for students and staff.
ASPHALT WORKS SPECIFICATIONS
Asphalt construction work specifications refer to the guidelines and requirements for the construction and installation of asphalt surfaces. It is important that the contractor is aware of and adheres to these specifications to ensure that the final product meets the necessary standards and will be durable and safe for its intended use. Some key specifications that may be included are:
Full depth site excavation: This involves removing the existing surface of the road along with any underlying layers, such as subgrade or subbase, down to the required depth. This is typically done to repair or replace the road foundation.
- Road surface profiling and resheeting: Profiling is the process of removing the upper surface of a road using a milling machine to create a smooth surface. Resheeting involves the installation of a new asphalt surface layer over the existing road base or subbase.
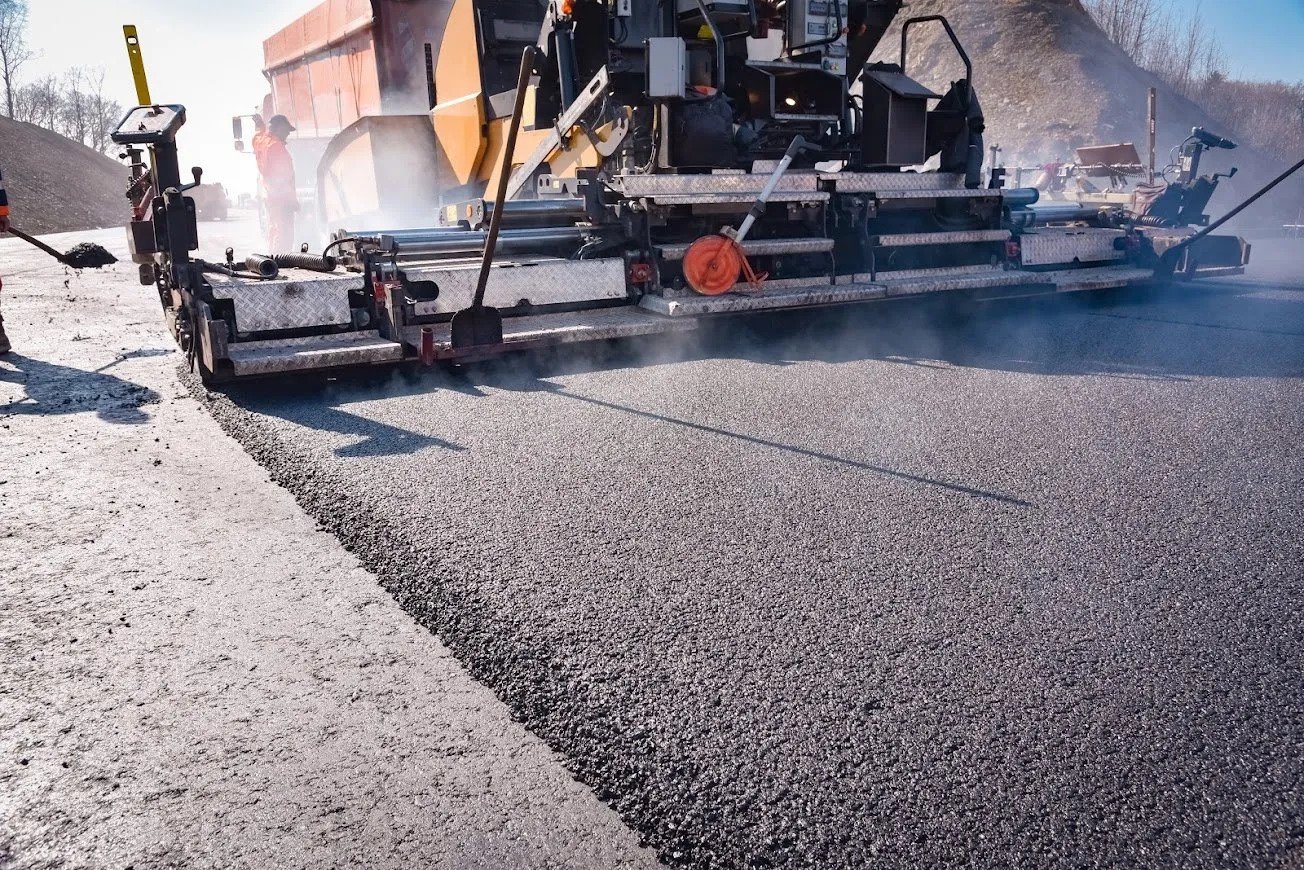

This can be done to repair and maintain the surface of an existing road.
- Asphalt product selection and installation: The asphalt products used in road construction vary in density, depending on the intended use and the traffic volume of the road. Low-density asphalt products are typically used for low-volume roads, while high-density products are used for heavily-trafficked roads.
- Asphalt product selection and installation: The asphalt products used in road construction vary in density, depending on the intended use and the traffic volume of the road. Low-density asphalt products are typically used for low-volume roads, while high-density products are used for heavily-trafficked roads.
- Raising and resetting of stormwater grate pits: Stormwater grated pits are designed to collect and channel away excess water from roads. These pits can become blocked over time, so raising and resetting them involves removing the existing pit and replacing it with a new one.
- Pavement repair and rebuilding: This refers to the process of repairing or rebuilding a road surface that has become damaged or worn over time. Pavement rehabilitation may involve fixing specific areas of damage or resurfacing the entire road. Pavement reconstruction, on the other hand, involves removing and replacing the entire surface of the road.

APPLICATIONS OF ASPHALT
- Road Construction – Asphalt is the primary surface material for highways, roads, streets, and other pavements. It is mixed with aggregate (such as crushed rock or gravel) to form asphalt concrete, which is then used to pave roads. The asphalt binds the aggregate together and provides a smooth surface for vehicles to travel on.
- Parking Lots – Asphalt is a popular material for constructing parking lots because it is relatively inexpensive, durable, and easy to install. It is also flexible and able to withstand the constant movement and heavy weight of vehicles. Asphalt parking lots require regular maintenance, including sealcoating, patching, and crack filling, to ensure that they remain in good condition for a long period of time.
- Driveways: Asphalt is also often used for residential driveways, as it is more durable than concrete and can withstand the weight of cars, trucks,
and other vehicles. Driveways are a common use case for asphalt, as the material is both durable and affordable. Asphalt is a prominent choice for driveways since it can withstand the weight of vehicles, including cars, trucks, and SUVs, as well as the wear and tear from daily use.
- Airport Runway: Asphalt is a composite material commonly used for airport runways because it is durable, strong, and able to withstand the heavy loads and constant use of aircraft traffic. The smooth surface of asphalt also provides good traction for aircraft during takeoff and landing, and its flexibility allows it to withstand changes in temperature and weather conditions. Additionally, asphalt is relatively inexpensive and easy to repair, making it a cost-effective option for airport runway construction.
- Sport Courts: Asphalt is a popular choice for building sports surfaces, such as running tracks and basketball courts, due to its durability, smooth surface, and ability to withstand heavy usage. Running tracks made of asphalt provide a smooth and consistent surface for athletes to run on and are typically made from a mixture of asphalt and a rubberized material, such as granulated tyre rubber or synthetic rubber. They also come in a variety of thicknesses, allowing for different levels of hardness depending on the athletic activities that will be performed on them.
BENEFITS OF ASPHALT
- Durability: Asphalt is a strong and durable material that can withstand heavy loads and extreme temperatures. The materials used to make asphalt (bitumen and aggregate) are mixed together to create a surface that is strong enough to withstand the weight of vehicles, and resist deformation or cracking caused by changes in temperature and weather conditions. Asphalted roads typically have a long lifespan, with regular maintenance prolonging their life even further.
- Cost-effectiveness: Asphalt is typically less expensive than concrete and requires less maintenance over time. The cost of materials and labour for asphalt is lower compared to concrete, and once it’s in place, it requires minimal upkeep. Additionally, it can be

maintained by simple resurfacing rather than reconstruction of the entire road.
- Easy to install and repair: Asphalt can be installed quickly and easily, and small repairs, such as potholes, can be made with minimal disruption. The process of laying asphalt is relatively simple and doesn’t require specialised equipment or training. Additionally, small repairs and patching can be done by simple processes such as heating and compacting, which can be done with minimal disruption to traffic.
- Recyclability: Asphalt can be recycled, which reduces waste and the overall environmental impact of road construction. Asphalt can be ground up and reused in new road construction or repair projects. This reduces the amount of new materials needed, and also helps to reduce the environmental impact of road construction.
- Low Noise: The asphalt road surface provides a smooth, quiet ride for drivers, reducing traffic noise. The smoothness and tightness of the surface, along with its ability to deaden sound, make it a more pleasant surface for nearby residents, which is beneficial for residential areas.
- Flexibility: Asphalt is a flexible material that can be moulded to fit a variety of different surfaces and designs. It can be used in new construction as well as overlaid on existing roads. The flexibility of asphalt makes it suitable for a wide variety of road types, including highways, city streets, and residential roads.
- Safe driving surface: Asphalt has good skid resistance, which makes it safer for vehicles to drive on. The rough surface of asphalt provides a good grip for tires, reducing the risk of skidding or slipping, especially during wet weather conditions. This can help prevent accidents and improve the overall safety of the road for drivers.
Difference between Asphalt and Concrete
| Asphalt | Concrete |
|---|---|
| Dark-coloured, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum | A solid, stone-like material made from cement, water, and aggregate materials |
| Primarily used in road construction | Widely used in construction for foundations, buildings, bridges, and roads |
| Made of Bitumen (a by-product of crude oil refining) and aggregate (crushed stone, gravel, sand) | Mixture of cement, water, and aggregate (crushed stone, gravel, sand) |
| Soft and pliable when first laid, hardening over time | Hard and durable immediately after installation |
| Resistant to fuel and oil spills | Resistant to heavy loads and extreme weather conditions |

